Introduction
Health insurance is a critical component of personal finance, offering protection against unexpected medical expenses. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of finding the cheapest health insurance that suits your needs. From understanding the basics to exploring cost-saving strategies, let’s navigate through the complex world of healthcare coverage together.
Understanding Health Insurance
Health insurance serves as a financial safety net, covering medical expenses ranging from routine check-ups to emergency surgeries. It comes in various forms, including individual plans, family plans, and employer-sponsored coverage. Understanding the types of health insurance and their coverage options is crucial for making informed decisions.
- What is health insurance? Health insurance is a contract between an individual and an insurance provider, wherein the insurer agrees to cover a portion of the policyholder’s medical expenses in exchange for regular premium payments.
- Types of health insurance There are several types of health insurance, including Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs), and Point of Service (POS) plans. Each type varies in terms of provider networks, coverage flexibility, and out-of-pocket costs.
- Coverage options Health insurance plans offer different levels of coverage, including preventative care, prescription drugs, hospitalization, and specialty services. Understanding your healthcare needs and selecting a plan that provides adequate coverage is essential for managing costs effectively.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
The cost of health insurance can vary significantly based on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you anticipate expenses and make informed decisions when selecting a plan.
- Age and health status Younger and healthier individuals typically pay lower premiums than older adults or those with pre-existing medical conditions. Insurance companies assess risk based on age, health history, and lifestyle factors, which can impact premium rates.
- Location Health insurance costs vary by geographic region due to differences in healthcare market dynamics, provider availability, and local regulations. Urban areas often have higher premiums than rural areas due to increased demand for healthcare services.
- Coverage options and deductibles The level of coverage you choose and the size of your deductible can significantly impact your health insurance costs. Plans with higher deductibles typically have lower premiums but require higher out-of-pocket expenses for medical care.
- Provider networks Insurance plans may have different provider networks, ranging from narrow networks with a limited selection of healthcare providers to broad networks that offer more extensive coverage options. Choosing a plan with a network that includes your preferred doctors and hospitals can affect costs.
Finding the Cheapest Health Insurance
Navigating the health insurance marketplace can be overwhelming, but with the right approach, you can find affordable coverage that meets your needs.
- Researching available plans Start by researching available health insurance plans in your area. Websites like Healthcare.gov and state-based exchanges provide information on available plans, premiums, and coverage options. Compare plans based on cost, coverage, and provider networks to find the best fit for your budget and healthcare needs.
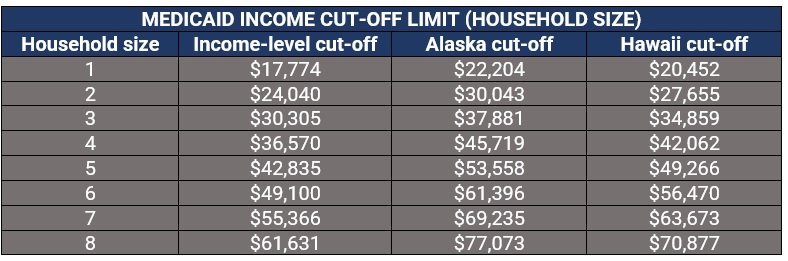
- Utilizing government resources Government programs like Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) offer low-cost or free health insurance coverage to eligible individuals and families. Determine if you qualify for these programs based on income and other eligibility criteria.
- Considering alternative options In addition to traditional health insurance plans, consider alternative options such as short-term health insurance, health sharing ministries, and direct primary care arrangements. These alternatives may offer lower premiums or more flexible coverage options, depending on your needs and circumstances.
Tips for Reducing Health Insurance Costs
Even if you’re already enrolled in a health insurance plan, there are several strategies you can employ to lower your healthcare costs and maximize value.
- Comparison shopping Regularly review your health insurance options to ensure you’re getting the best value for your money. Compare premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and coverage limits to identify potential savings opportunities.
- Adjusting coverage levels Evaluate your healthcare needs and consider adjusting your coverage levels accordingly. If you’re relatively healthy and don’t anticipate significant medical expenses, opting for a high-deductible plan with lower premiums may be a cost-effective choice.
- Utilizing employer-sponsored plans If your employer offers health insurance benefits, take advantage of these plans as they often provide competitive rates and comprehensive coverage options. Explore different plan choices and consider participating in wellness programs or health savings accounts to further reduce costs.
- Utilizing health savings accounts Health savings accounts (HSAs) allow you to save money for medical expenses on a tax-advantaged basis. Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, and funds can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses, including deductibles, co-pays, and prescription drugs. Maximize your HSA contributions to offset out-of-pocket healthcare costs and reduce your taxable income.
FAQ’s
1. What is the difference between HMO and PPO health insurance plans? HMO plans typically require you to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals for specialist care, while PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers without referrals but may have higher out-of-pocket costs.
2. Can I get health insurance if I have a pre-existing medical condition? Under the Affordable Care Act, health insurance companies cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. You have the right to obtain health insurance regardless of your medical history.
3. Are there any subsidies available to help lower health insurance costs? Depending on your income and household size, you may qualify for premium tax credits or subsidies through the health insurance marketplace to offset the cost of coverage. Visit Healthcare.gov to determine your eligibility and apply for financial assistance.
4. What is a health savings account (HSA), and how does it work? A health savings account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged savings account that allows you to set aside money for medical expenses. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and funds can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses tax-free. HSAs are available to individuals enrolled in high-deductible health plans (HDHPs).
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding the cheapest health insurance requires careful consideration of various factors, including coverage options, provider networks, and cost-saving strategies. By understanding your healthcare needs, researching available plans, and exploring alternative options, you can secure affordable coverage that provides peace of mind and financial protection. Remember to regularly review your health insurance options and adjust your coverage as needed to ensure you’re getting the best value for your money.



0 Comments